
Ali Rizvi
Article Understanding When to Record Revenue
ASC 606 outlines a 5-step process that businesses should follow to accurately recognize revenue. The entire process relies on satisfying contractual obligations.
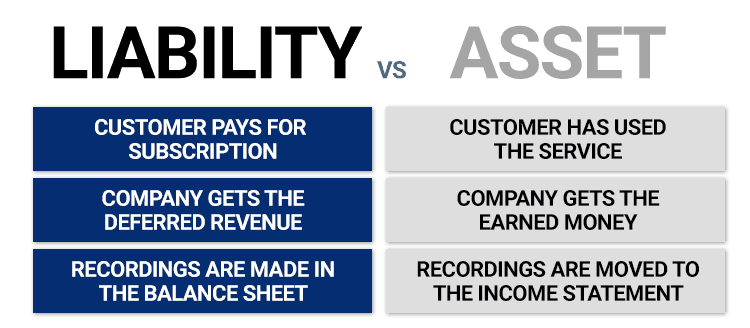
Revenue vs Deferred revenue
Revenue is money earned from delivering a product or service, while Deferred Revenue comes from prepayment for a good or service, so it is known as unearned.
Recording revenue is an integral part of running a successful business. Not only is it helpful to have revenue procedures in place to ensure a smooth month-end close, but generating accurate financial statements relies on proper revenue recognition (read more about rev rec from Deloitte here).
Understanding the primary difference between revenue and deferred revenue and when to record each is important to develop accurate and useful financial information for your growing business.
What is Revenue?
Revenue is the money earned from delivering a product or completing a service. Revenue is recorded on the income statement when the amounts are earned. Earned does not always translate to received. A business can earn revenue without seeing the cash in the bank. This is one of the core concepts of accrual accounting.
For example, let’s say your business is hired to install a software program. Once the software is installed and you’ve completed all of the duties outlined in your contract, you will issue an invoice to the customer. The customer may take a week or two to pay, but according to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, you have earned the revenue as soon as your work was done.
What is Deferred Revenue?
Deferred revenue, commonly referred to as unearned revenue, occurs when the customer prepays for a good or service. Deferred revenue is recorded as a liability on the balance sheet because your business may need to repay the deposit if the job is not completed. Once the job is complete, your business will move the amount from deferred revenue to earned revenue on the income statement.
Using the previous example, if the customer were to pay the invoice before you installed the software, you would record the amounts in deferred revenue until the job is complete.
Understanding When to Record Revenue
Since revenue directly impacts your business’s tax liability, the IRS closely monitors the amounts companies report through ASC 606. It's a 5-step process that businesses now must follow to accurately recognize revenue.
The entire process relies on satisfying contractual obligations. If your contracts with customers don’t have recognizable segments, it can be difficult to know when to record revenue or deferred revenue.
Core Principles Five-Step Revenue Recognition Process, SaaS or Otherwise
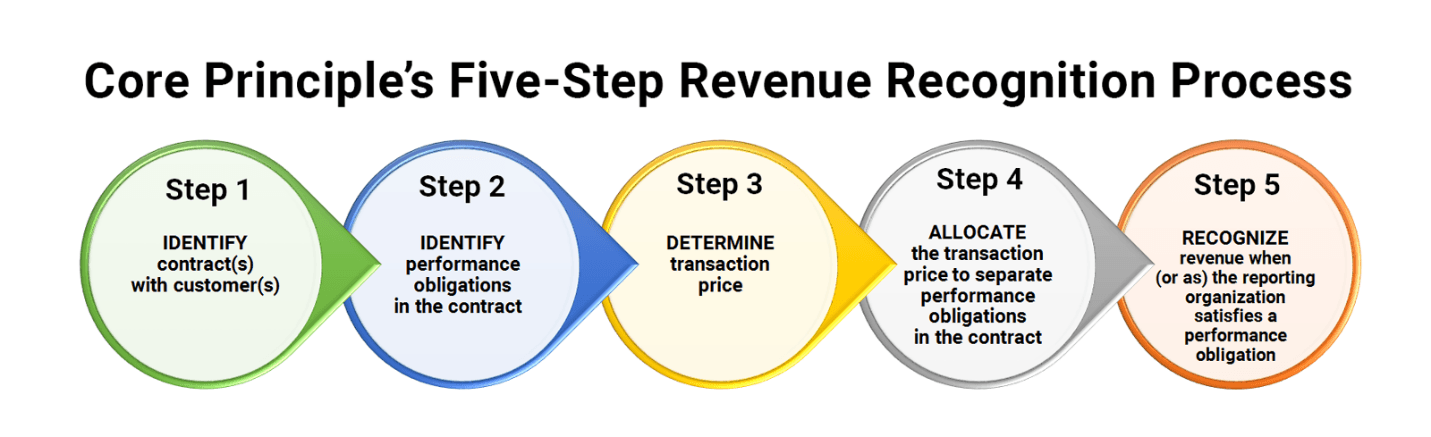
- Step 1 Identify contract(s) with customer(s)
- Step 2 Identify performance obligations in the contract
- Step 3 Determine transaction price
- Step 4 allocate the transaction price to separate performance obligations in the contract
- Step 5 Recognize revenue when (or as) the reporting organization satisfies a performance obligation
Identify each contractual obligation in a contract with a customer and assign a price to each of those segments. This will help you move the correct amount to earned revenue after each obligation. ASC 606 defines performance obligations as being satisfied once control has passed from your business to the customer.
Applying ASC 606 to a real-life example can be beneficial. Let’s say that a customer contracts your business to install a new IT system and then maintain the system for 2 years. The first performance obligation would be installing the new IT system, while the other obligation would be system maintenance.
Although the customer might prepay for the entire contract, the portion allocated to system maintenance is not earned revenue but instead will be reported as deferred revenue until the obligation has been satisfied.
Summary
Want to see a demo?
we offer a 14-day free trial.
